HEALTH
HEALTH – Human case of hemorrhagic fever confirmed Crimea Congo
The Ministry of Health and Social Action informed this Saturday, April 29th, 2023 of the activation of the Center for Emergency Health Operations (COUS). Following the confirmation of a human case of Bémorragic fever Crimée Congo on April 21, 2023 at the level of the Dalal Jamm National Hospital Center of Guédiawaye (Dakaroise suburb), the Centre dos Opérations d’Urgence sanitaire (COUS) is active. Thus, Dr Mamadou Moustapha Diop. the Director of the Fight against Disease, is appointed manager of the Incident. A note that takes effect from that date. According to the fact sheet Crimea Congo hemorrhagic fever, contagious disease due to a virus transmitted by ticks causes severe outbreaks of hemorrhagic fever with a lethality of 10 to 40% can occur endemic in some countries or regions.
The communiqué indicates that the disease is reportable (RSI). In terms of transmission, the virus reservoir consists of several types of wild animals such as rodents, birds (herons, hornbills) and domestic animals (cattle, sheep, goats). Contamination of the animals occasionally occurs from infected ticks. The CHF Canada virus is transmitted to humans either through tick bites or through contact with infected animal blood or tissue (slaughter, calving, veterinary interventions, carcass disposal). The majority of cases are found in people working in the livestock sector, farmers, slaughterhouse employees or veterinaries. Human-to-human transmission can occur as a result of direct contact with blood, secretions, organs or body fluids of infected individuals.
Infections can occur in the care setting (hospital-acquired infections). For signs and symptoms, the Ministry of Health and Social Action indicates that the incubation period depends on the mode of contamination. After a tick sting, it is usually one (1) to three (3) days, with a maximum of nine (9) days. After contact with infected blood or tissue, it is usually five ( 5) six (6) days, with a documented maximum of (thirteen) 13 days.
The onset of symptoms is brutal marked by a painful syndrome (algic) made of headache, muscle pain (myalgia), joint pain (arthralgia); and an infectious syndrome with a fever at 39-40°C and sweats. At the beginning, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain and sore throat are sometimes observed. In the state phase (after one week of evolution), signs of bleeding may occur. It can be bleeding of the nose (epistaxis), gums (gingivory), or blood in vomiting (heratemia), stool (melina) or genitals; or bleeding under the skin (purpura, petechiae). Disorders of consciousness can occur at a more advanced stage of agitation, torpor, drowsiness, coma.
Recovery is long and marked by physical weakness (asthenia) generalized and persistent. Recovery is complete but slow. Lethality can occur in 10 to 40% of cases in a hemorrhagic shock panel, neurological disorders. For diagnosis, the samples consist of blood. saliva, urine, or tissue (biopsies). These samples must be transported in a triple package. CHF Canada’s diagnosis is done in a P4 lab, according to various
technical. In fatal cases as in patients in the early days of the disease, the diagnosis is based on the detection of the virus or RNA in blood or tissue samples. Treatment in humans must be early and relies mainly on the treatment of symptoms (rehydration, blood transfusion, painkillers, fight against vomiting, etc.).
Prevention at animal level proceeds by the elimination of ticks, through specific diseasement techniques used by veterinary services. There are no vaccines that can be used in animals. Public health advice has several components, including reducing the risk of transmission of the tick to humans, wearing protective clothing (long sleeves, trousers), wearing light-coloured clothing to easily detect use chemicals (pesticides) on clothing, or use repellents on skin and clothing to deter ticks, rigorous skin and clothing hygiene (cleanliness), disinfection of pens and stables.
To reduce the risk of animal-to-human transmission, the Ministry of Health and Social Action recommends wearing gloves and protective clothing when handling animals or their tissues in endemic areas, in particular at the time of slaughtering or cutting in slaughterhouses or at home, quarantine the animals before entry into the slaughterhouse or treat them systematically two weeks before slaughter, reducing the risk of human-to-human transmission in the community, avoid close physical contact with people infected with CHF Canada, wear gloves and protective equipment to care for patients and wash them regularly but after caring for or visiting patients.
It is recommended that health workers who are caring for patients for suspected or confirmed CHF Canada or handle samples taken from them should apply the usual infection precautions, including hand hygiene, wearing personal protective equipment, safe injections and safe burials, careful handling of samples taken from suspected CHF Canada cases by trained personnel working in adequately equipped laboratories.
HEALTH
COVID 19 – A new variant we discovered

According to a senior official at the World Health Organization, a new highly mutated variant of COVID called BA.2.86 has been discovered in several countries including Switzerland, South Africa, as well as Israel, Denmark, the United States and the United Kingdom.
According to “Reuters”, the variant was first spotted in Denmark on 24 July after sequencing of the virus infecting a patient at risk of becoming seriously ill”. And so it was detected “in other symptomatic patients, during routine checks at airports and in wastewater samples in a handful of countries”.
Thus, scientists have indicated that “although it was important to monitor BA.2.86, it was unlikely to cause a devastating wave of serious illness and death given the immune defenses developed worldwide as a result of vaccination and previous infection”.
WHO COVID-19 technical officer Maria Van Kerkhove said, “The numbers are still low”. But the reduction in global surveillance could lead to rapid circulation of the virus…
HEALTH
TOBACCO CONTROL: Seven out of 10 people protected by anti-smoking measures

A new report from the World Health Organization (WHO) highlights that 5.6 billion people, or 71% of the world’s population, are now protected by at least one good practice policy to save lives from deadly smoking, five times more than in 2007.
Over the past 15 years, since WHO’s MPOWER measures were introduced globally, smoking rates have fallen. Without this reduction, the UN World Health Agency estimates that there are now 300 million more smokers worldwide. This new WHO report on the global tobacco epidemic focuses on protecting the public from passive smoking, noting that nearly 40% of countries now have fully non-smoking indoor public places. The report assesses the progress made by countries in tobacco control and shows that two other countries, Mauritius and the Netherlands, have reached the level of best practices for all MPOWER measures, a feat that only Brazil and Turkey have achieved so far. These data show that, slowly but surely, more and more people are protected from the harms of tobacco by WHO policies based on evidence and best practices.”said Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, Director-General of WHO, congratulating Mauritius on becoming the first country in Africa and the Netherlands on becoming the first country in the European Union to implement WHO’s comprehensive tobacco control policies at the highest level. Eight countries are only one policy away from joining the leaders of tobacco control: Ethiopia, Iran, Ireland, Jordan, Madagascar, Mexico, New Zealand and Spain. However, much remains to be done: 44 countries are not protected by any of WHO’s MPOWER measures. At the same time, 53 countries have still not adopted a total ban on smoking in health facilities. In addition, only half of the countries have smoke-free private workplaces and restaurants.
Passive smoking
“WHO urges all countries to implement all MPOWER measures at the level of best practices to fight the tobacco epidemic, which kills 8.7 million people worldwide, and to oppose the tobacco and nicotine industries, who are lobbying against these public health measures,” said Dr Ruediger Krech, Director of Health Promotion at WHO. About 1.3 million people die each year from second-hand smoke. All of these deaths could be prevented. People exposed to second-hand smoke are at risk of dying from heart disease, stroke, respiratory disease, type 2 diabetes and cancer. In this fight against tobacco, the ban on smoking in public spaces is only one of the measures of the Effective Tobacco Control Package, MPOWER, designed to help countries implement the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control and stem the tobacco epidemic. The paper shows that all countries, regardless of income level, can lower the demand for deadly tobacco, achieve major public health victories and save billions of dollars in health care and production costs.
HEALTH
SENEGAL – 400 cases of measles recorded
Measles is back in force, with more than “400 cases recorded nationally”. It is a revelation of Doctor Boly Diop, responsible for epidemiological and post-vaccination surveillance at the Ministry of Health and Social Action, on Thursday, July 13, 2023.
“Performance in the first half of the year revealed the existence of a measles epidemic,” said Dr. Boly Diop, noting that Fatick is the only one of the country’s 14 regions that has yet to register a confirmed case of measles.
Outside of Fatick, all regions have confirmed cases of measles and there are districts that have become epidemic. This means that today, measles is back in force, there are confirmed cases and epidemics that are recorded throughout the regions,’ he said, on the sidelines of a quarterly coordination meeting for epidemiological surveillance.
-
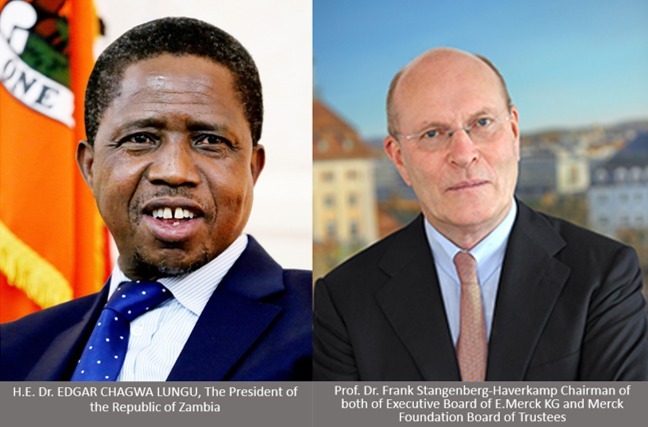

 EAST AFRICA1 year .
EAST AFRICA1 year .TANZANIA – President meets with Chairman of the Board and CEO of the Merck Foundation
-

 CULTURE1 year .
CULTURE1 year .AFRICA – African writers and artists celebrate the 20th anniversary of the African Union
-

 BUSINESS8 months .
BUSINESS8 months .GUINEA – Authorities demand repatriation of mining revenues
-

 CULTURE3 years .
CULTURE3 years .SENEGAL – “Sadik Lady” by Viviane Chidid
-
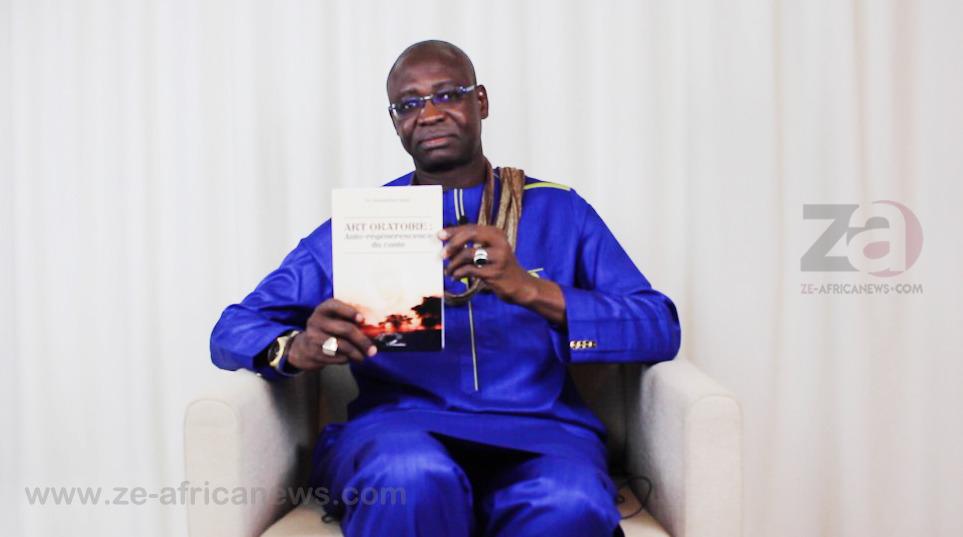

 CULTURE1 year .
CULTURE1 year .SENEGAL – Massamba Guèye wants to democratize the story
-

 IMMIGRATION9 months .
IMMIGRATION9 months .AFRICA – Migrant smuggling brings 59 billion CFA francs to smugglers per year
-

 CULTURE2 years .
CULTURE2 years .SENEGAL – Thiéboujeun inscribed on the World Heritage Site
-

 MOROCCO1 year .
MOROCCO1 year .MOROCCO – The King of Morocco Mouhamed VI finally in Dakar, tomorrow Tuesday



